Back بوابة:إنترنت Arabic دەروازە:ئینتەرنێت CKB Portál:Internet Czech Portal:Internet German Portal:Internet Spanish درگاه:اینترنت Persian Portail:Internet French פורטל:אינטרנט HE Պորտալ:Համացանց Armenian Portal:Internet ID
The Internet PortalThe Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a network of networks that consists of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the interlinked hypertext documents and applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), electronic mail, internet telephony, and file sharing. The origins of the Internet date back to research that enabled the time-sharing of computer resources, the development of packet switching in the 1960s and the design of computer networks for data communication. The set of rules (communication protocols) to enable internetworking on the Internet arose from research and development commissioned in the 1970s by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) of the United States Department of Defense in collaboration with universities and researchers across the United States and in the United Kingdom and France. The ARPANET initially served as a backbone for the interconnection of regional academic and military networks in the United States to enable resource sharing. The funding of the National Science Foundation Network as a new backbone in the 1980s, as well as private funding for other commercial extensions, encouraged worldwide participation in the development of new networking technologies and the merger of many networks using DARPA's Internet protocol suite. The linking of commercial networks and enterprises by the early 1990s, as well as the advent of the World Wide Web, marked the beginning of the transition to the modern Internet, and generated sustained exponential growth as generations of institutional, personal, and mobile computers were connected to the internetwork. Although the Internet was widely used by academia in the 1980s, the subsequent commercialization of the Internet in the 1990s and beyond incorporated its services and technologies into virtually every aspect of modern life. (Full article...) Selected article
4chan is an English-language imageboard website based on the Japanese-language Futaba Channel. Launched on October 1, 2003 by "moot" ("Christopher Poole"), its boards are based primarily around the posting of pictures and discussion of Japanese comics and television shows. Users generally post anonymously, and the site has been linked to "Anonymous" culture and Project Chanology. 4chan's "/b/" board, dedicated to random postings, is the most active and is notorious on the Internet. The site has generated significant media attention, and its members have been responsible for the formation and popularization of several Internet memes such as lolcats, rickrolling, and the popularity of the Tay Zonday song "Chocolate Rain". It has also received media attention for its attacks against other websites and Internet users, and for the threats of real world violence that have been posted on it.
Selected picture A blog (a portmanteau of web log) is a website where entries are commonly displayed in reverse chronological order. "Blog" can also be used as a verb, meaning to maintain or add content to a blog. Many blogs provide commentary or news on a particular subject; others function as more personal online diaries. A typical blog combines text, images, and links to other blogs, web pages, and other media related to its topic. Hightail, formerly YouSendIt, is a cloud service that lets users send, receive, digitally sign, and synchronize files. YouSendIt.com and YouSendIt Inc. were founded in 2004; the company renamed itself Hightail in 2013. The company's early focus was on helping users send files that were too large for email; it started adding features and plug-ins for businesses in 2007. The service grew quickly, and the firm raised $49 million in funding between 2005 and 2010. The service can now be used via the web, a desktop client, mobile devices, or from within business applications using a Hightail plugin. In May 2015, the company launched Hightail Spaces, designed to encourage creative professionals from conception of an idea to delivery. In 2018, Hightail was acquired by OpenText. (Full article...) WikiProjects
Did you know (auto-generated) -
Selected biography
William Ford Gibson, born March 17, 1948, in Conway, South Carolina is an American-Canadian writer who has been called the "noir prophet" of the cyberpunk subgenre of science fiction. Gibson coined the term cyberspace in 1982, and popularized the concept in his debut novel, Neuromancer (1984). In depicting a visualised worldwide communications network before the ubiquity of the Internet, Gibson is credited with anticipating important aspects, and establishing the conceptual foundations, of the Internet and the Web in particular. Although much of Gibson's reputation has remained rooted in Neuromancer, his work has continued to evolve conceptually and stylistically. After expanding on Neuromancer with two more novels to complete the dystopic Sprawl trilogy, Gibson became central to an entirely new science fiction subgenre—steampunk—with the publication in 1990 of the alternate history novel The Difference Engine, written in collaboration with Bruce Sterling. In the 1990s he composed the Bridge trilogy of novels, which focused on sociological observations of near future urban environments and late stage capitalism. His most recent novels—Pattern Recognition (2003), and Spook Country (2007)—are both set in a contemporary universe and have put Gibson's work onto mainstream bestseller lists for the first time.
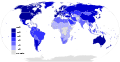
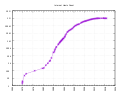
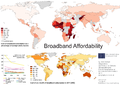
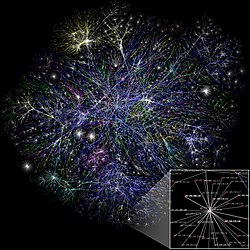
General images -The following are images from various internet-related articles on Wikipedia.
Selected quoteMain topics
Featured contentCategoriesRelated portalsThings you can do
Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Wikipedia's portals |